Road maintenance is such an important issue that the implications are nowadays also of political nature. Very often the poor state of maintenance affects our roads safety as well as the ride comfort. In an advanced country, no exception should be allowed even on the latter, but certainly safety is the top priority.
![]() Per la versione in Italiano: https://www.stradeeautostrade.it/attrezzature-e-componenti/la-rigenerazione-a-freddo-in-sito-dellasfalto-ammalorato-per-un-immediato-ripristino/
Per la versione in Italiano: https://www.stradeeautostrade.it/attrezzature-e-componenti/la-rigenerazione-a-freddo-in-sito-dellasfalto-ammalorato-per-un-immediato-ripristino/
The concept of road maintenance is related to pavement life cycle.
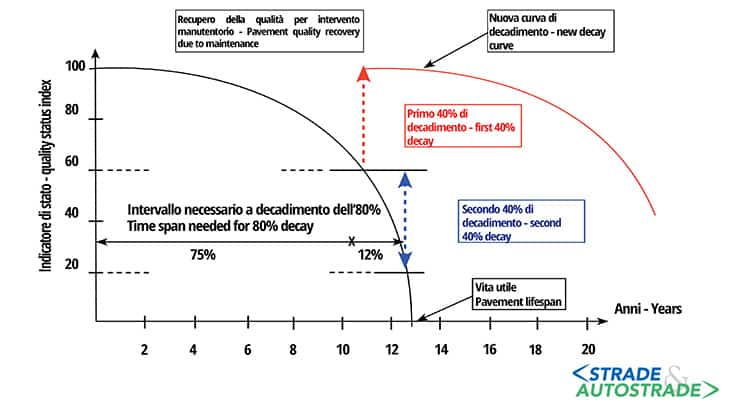
The following diagram (Figure 1) is one of many available in literature. Simply explained, it means that doing tomorrow what should be done today is much more expensive for Authorities, therefore ultimately for the tax payer, and penalizing for users.
The structural requirements of a pavement include the bearing capacity (necessary to withstand vehicle loads) and durability intended as resistance to degradation. The functional requirements include the grip between tires and the rolling surface and the evenness of road surface; therefore, strictly connected to driving comfort and safety.
The concept is certainly not new for professionals and on major roads maintenance is part, although often not to the extent needed, of managing protocols. The so-called minor roads are quite different; as the term minor indicates a mere technical category which, however, does not necessarily reflect the priority within the given community.
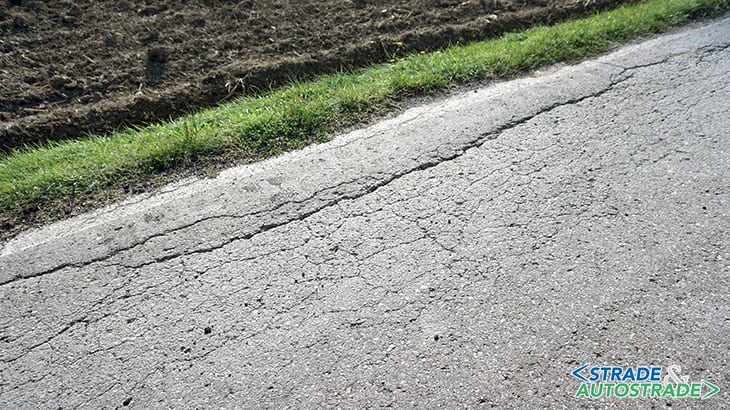
In essence, we get used to the fact that the roads must be short-lived, not very comfortable and safety delegated only to the due care of drivers. Thus often, notwithstanding life pavement cycle concept, we see little and poor maintenance, only when situations become unsustainable or dangerous.
Then the usual cold asphalt patch laid with a shovel (due to last a few months if not weeks), the absence of sealing in due time, and lastly the laying of a new wearing course on inadequate surfaces or, worse, on roads with deep structural weakness.
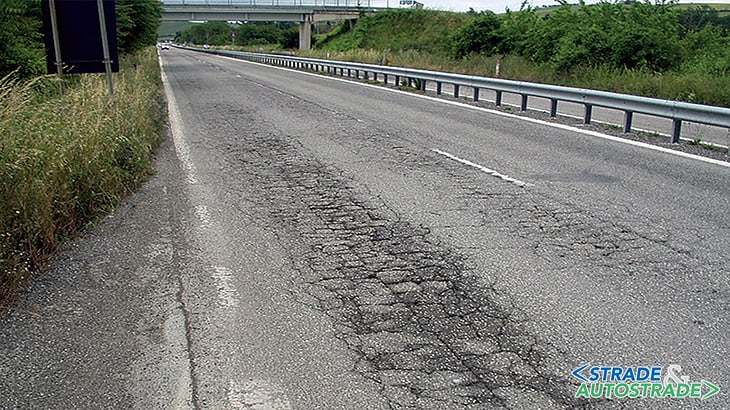
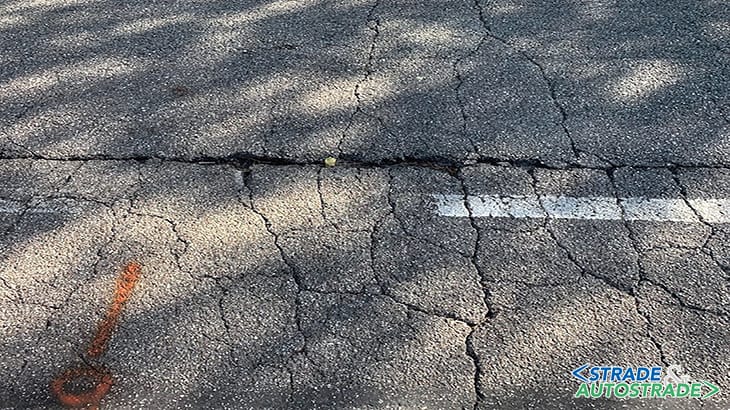
These are not solutions rather, at best, palliatives that in any case generate costs but for a very marginal result. There are many types of pavement distress and those are well described in technical literature. As an example, a brief summary follows (https://bit.ly/3ZHNOpq).
Types of pavement distress
Flexible pavement distresses can be grouped in some broad categories:
- cracks, depending on type and cause, can be referred to as crocodile cracks, blocks, reflective cracks and others;
- unevenness such as deformations, rutting, shearing, depressions, bulges;
- stripping, detachments, potholes;
- loss of skid resistance due to bleeding or polishing.
As obvious as it may sound, one should bear in mind that a road pavement is a structure and not a simple two-dimensional “strip”; a structure subjected to different loads and stresses and consequently to deformations of various kinds. Unfortunately, that often seems to be forgotten when we observe the current maintenance on our roads, on the secondary ones at least.
Municipalities have limited resources and they therefore try to restore large areas with the little resources available; however, spreading a maintenance budget on an areal basis rather than on the basis of technical priorities does not generate real solutions, at most it mitigates and postpones the problem.
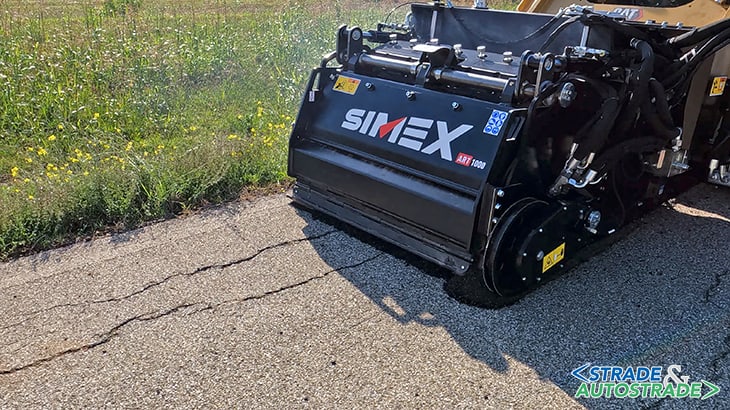
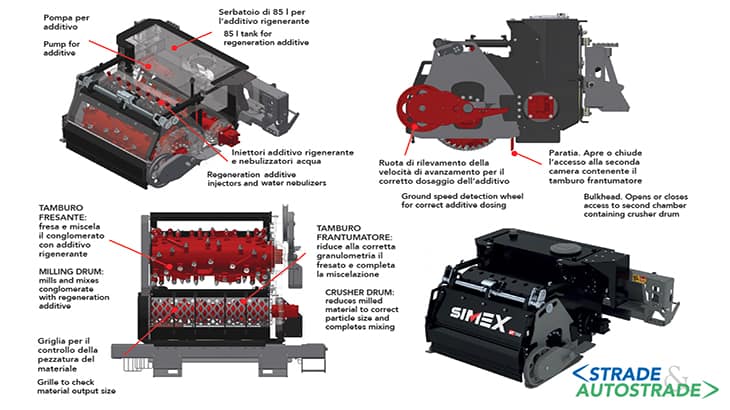
The ART 1000 proposal: a Simex patent
With the above in mind, Simex intended to design an equipment capable of ordinary maintenance with the following objectives, difficult to find in the market today:
- quality of solution;
- durability of the rehabilitation;
- possibility of recycling the material thus produced in subsequent processes;
- no environmental impact.
In essence, road repairs that can last an extended period of time, ensuring safety and ride comfort with an operational flexibility not available on the market.

Specifically, Simex has decided to develop a technology with an operative depth between 30 and 100 mm. Starting from the well-established self-leveling milling technique of the PL series (planers), it makes use of an ecofriendly chemical rejuvenator to regenerate, through a cold process, the RAP produced.
In cooperation with the Department of Civil, Chemical, Environmental and Materials Engineering of the University of Bologna – various laboratory and site tests were carried out,proving the effectiveness of the approach.
The equipment, now available on the market, was previewed at ASPHALTICA in November 2021 (in the form of advanced prototype) and subsequently at BAUMA 2022 in its final version, with the improvements derived from the numerous tests in the field.

The functioning of Simex method
Simex ART takes care of all the process with a single attachment. A dynamic and smaller construction site where no large machines are required, which significantly reduces traffic disruption. A reduced number of workers and a single vehicle (truck) which transports all the equipment on site.
The equipment, advancing to a certain milling depth, combines the following phases:
- milling of the damaged road section;
- controlled injection 1 of the rejuvenator in the milling chamber;
- size reduction of the milled material;
- mixing, obtaining the recycled RAP (reclaimed asphalt pavement) ready for road resurfacing.
1 The injection of the rejuvenator is controlled by a mechatronic system which regulates the quantity of injected rejuvenator according to depth and ground speed in order to maintain a defined percentage of rejuvenator with respect to the mass of milled asphalt.

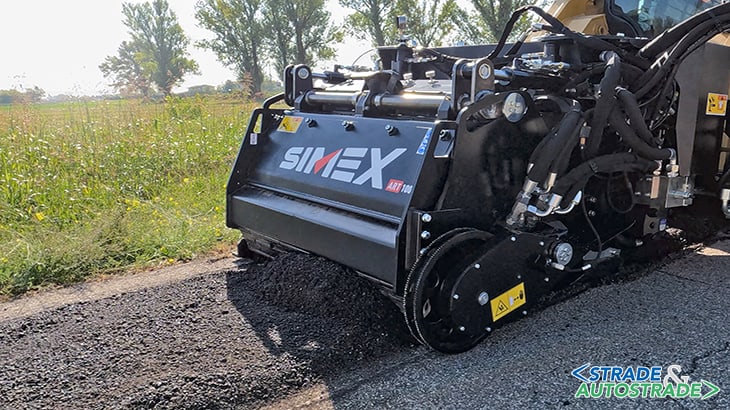
After being regenerated, the mix is laid directly by the equipment on the milling track and is ready to be leveled and compacted with a roller or vibrating plate.
Operating method
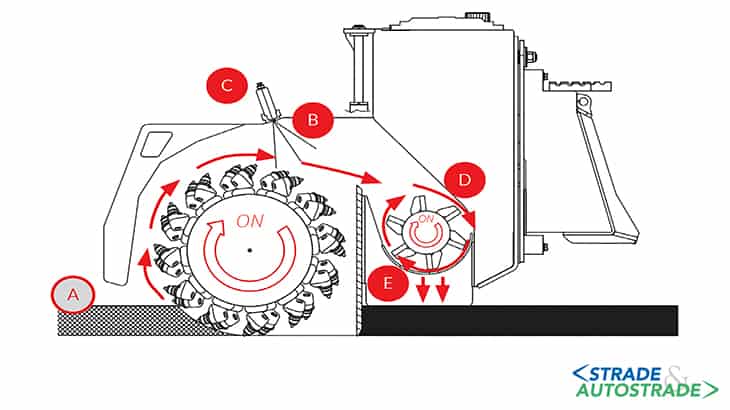
Milling (A) from 30 to 100 mm depth (hydraulic adjustment), depending on extent of distress. Milled material is mixed with rejuvenator contained in the tank (B) and nebulized (C) at high pressure using special pump. Mixed milled material goes into second chamber where crusher drum (D) reduces to correct particle size and further mixes it. Output grille (E) checks the obtained size (0-15 mm).
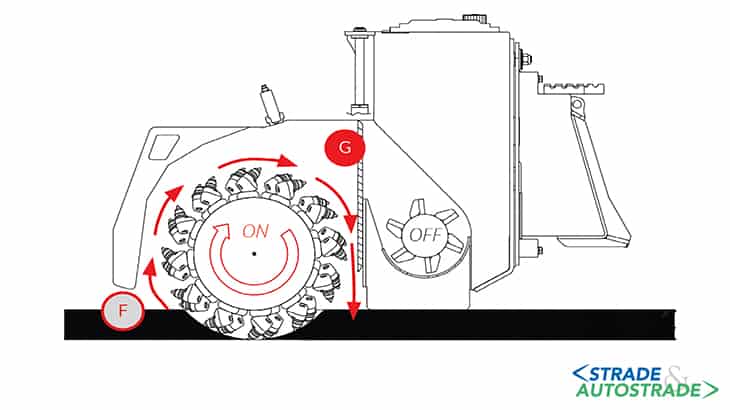
Nebulization is ensured by a Simex system that ensures maintaining the correct additive percentage depending on ground speed detected. It may be necessary to spray water using the integrated nebulization system (depending on type of additive used and conditions and type of asphalt to be resurfaced). Mixing (F) milled material obtained using milling drum. The chamber of the crusher drum is closed with special scraper (bulkhead) (G).
Once the activity of ART 1000 is completed, compaction comes next (plate or roller). The end result is a 100% regenerated bituminous conglomerate which, once compacted, can be driven on immediately.
Operational advantages
- Restoration of road surface distress, quickly and with long-lasting results, which allows for adequate road maintenance planning;
- a dynamic and smaller construction site: no large machines are required, which significantly reduces traffic disruption. A reduced number of workers and a single vehicle (truck) which transports all the equipment on site;
- money savings: zero costs for the procurement and transport of new mixes and virgin aggregates, in addition to not having to remove and dispose of the RAP;
- suitable for activity on surfaces of limited size.
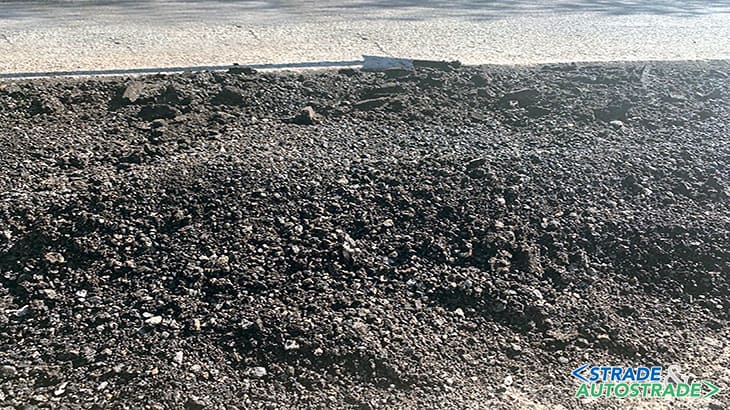

Environmental advantages
- No impact: pre-existing materials are reused, recycling and rehabilitating aged bitumen. Technically, this operation can also be repeated in subsequent maintenance operations;
- use of eco-friendly materials;
- no handling or management of special materials or waste;
- on site recycling saves energy if compared to traditional laying of hot mixes.
The mix
From what has been described one may easily recall the traditional in situ cold recycling; with two substantial differences however; the maximum thickness must be less than 10 cm and the road can be opened to traffic in a really short time without laying new material on top, such as a wearing course.
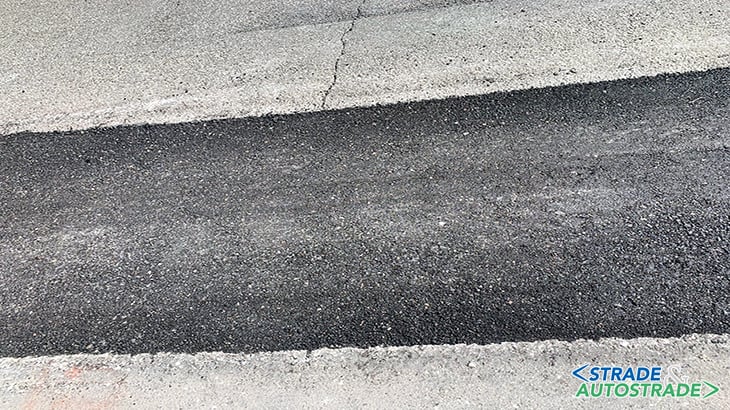

Bringing the concept of cold recycling at wearing course level, required a complete rethinking of the mix and the type of equipment. The structural cold recycling technique, with conventional emulsion or foamed bitumen, requires the subsequent laying of a new wearing course or binder layer for a base course. It also requires large machines that cannot be easily operated in urban or residential areas and with such a limited thickness.
Simex therefore envisaged a mix of calibrated size rap (10/12 mm max) added with a special regenerating admixture, to restore the characteristics lost over time, due to oxidation of the existing wearing course.
This type of product ensures the mix is environmentally friendly and that can be further recycled. Simex goal is to remain open to a wide range of products available in the market but at this stage it was necessary to rely on a widely tested product to eliminate the “chemical unknown”.
Thus, a partnership was born between Simex and Iterchimica in 2020, the Italian leading company in the road chemicals industry. The reader may refer to Iterchimica publications for technical information on their Iterlene HP Green (see “Strade & Autostrade” n. 126 November/December 2017 on page 76 ).
In a more advanced phase, ART has been tested by some companies of the road sector, using other rejuvenators of their own, with satisfactory results. The challenge arose, however, from the on-site application since previous experiences were all related to mixing in plant or by small concrete mixer with operational steps that are difficult to reproduce on site.
An example of application
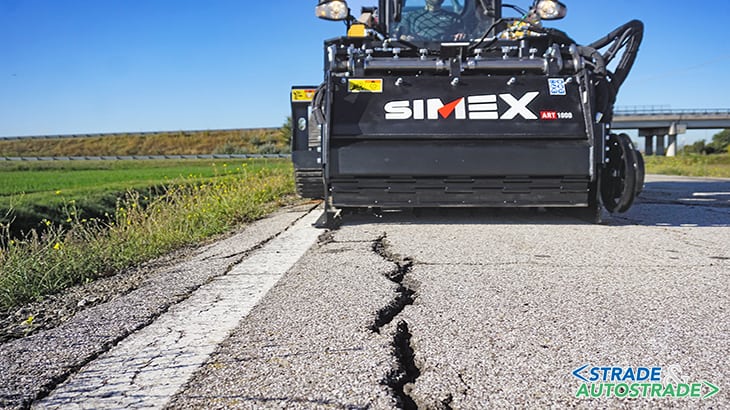
In order to validate the technology, various tests were carried out in the Bologna area, focusing in the first phase on minor types of roads. Although minor those are subject to significant residential and agricultural traffic developed on old rural road structures. Roads therefore lacking a real design and which have been paved often on poor subgrade.
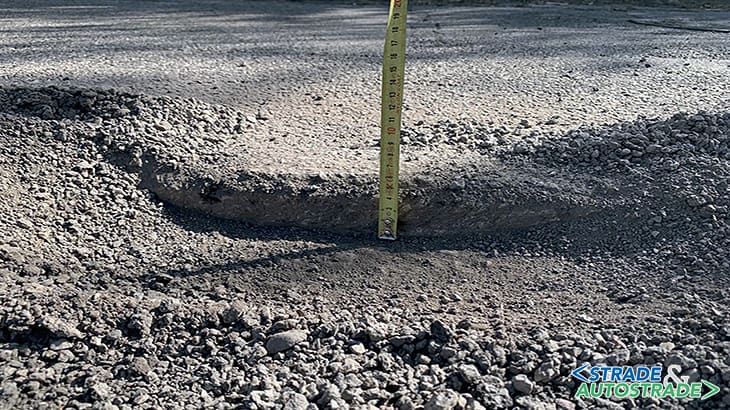
Over time they show various types of distress, causing cracks; hence the possibility for water and ice to carry out the subsequent action. Patches were then carried out with a width of 1 m and an average length of about 4/6 m each. The surface was trafficable after about 3 hours. A week later cores were taken to verify indirect tensile tests. All gave satisfactory results, above 0.20 N/mm2. A first indication that all was on the right track.
In a second, more advanced, phase the method was tested on medium-traffic roads but characterized by a significant transit of heavy vehicles linked to local industrial activities. Again, all the laboratory support was provided by the University of Bologna.

The following data are obtained from the thesis by Beatrice De Pascale “Innovative cold in-situ recycling of wearing course layers: laboratory and field characterization of 100% RAP asphalt concrete” for the achievement of the Master’s degree at the DICAM of the University of Bologna in the academic year 2020/2021 which takes into consideration several experimental sites.
As an example, the job site within the Municipality of San Giovanni in Persiceto (via Astengo) is reported here. The pavement was characterized by an evident cobweb of cracks affecting the entire width of the carriageway.
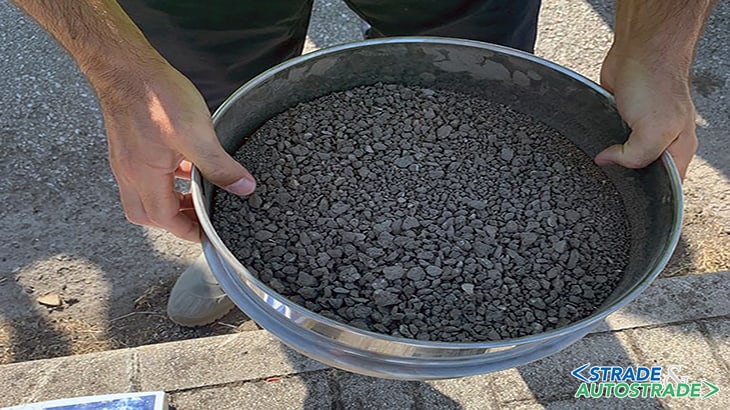
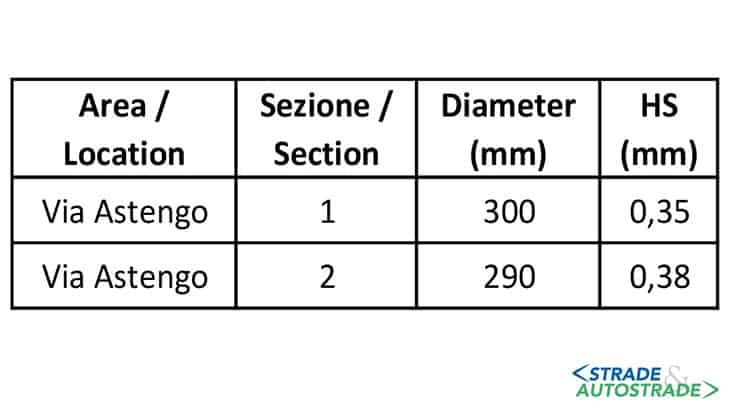
The working width is 1 meter and the repair length 8 m. It took 1 hour and a half to rehabilitate that stretch with no handling of materials and marginal labour. The material resulting from the first phase of milling is shown in the photo. Being the repair works relevant to the wearing course only, the machine was set at a depth of 5 cm.
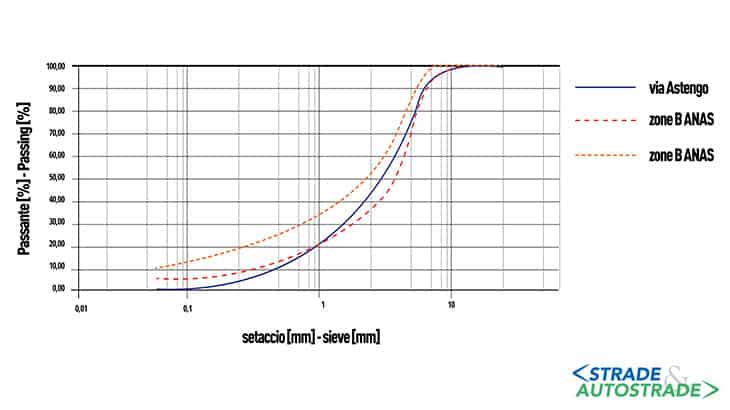
Size distribution analysis was carried out, shown in Figure 9, using the 1 mm reference sieve; the percentage of passing material was approximately 17%. That is in accordance with the target set in the mix design phase; also indicating that equipment is capable of delivering the rap according to an adequate particle size distribution.
Before starting the second phase, workers laid 1.5% of Portland 32.5 cement and machine was set up for delivering 2.5% of chemical additive. The mixed product after the second step highlights good homogeneity and good dispersion of the admixture.
Once this phase is completed, the material is leveled manually with a special equipment to ensure an even surface. Compaction followed by a compact 600 kg tandem roller.
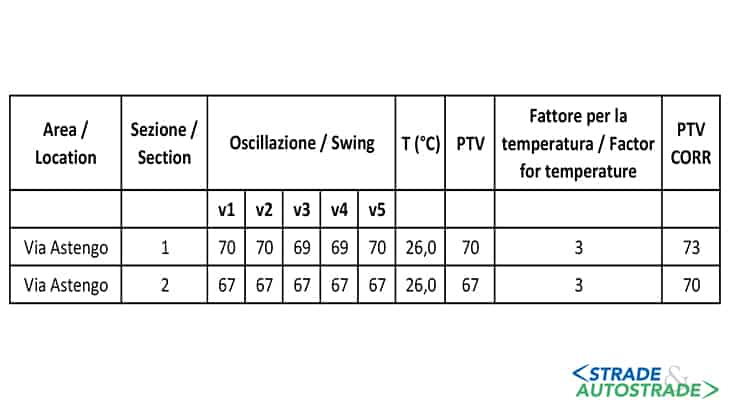
The road was then opened to traffic. A few hours for laying and curing are certainly advantageous but the material immediately develops all the mechanical properties necessary to ensure safe traffic flow. Grip test was also carried out for this purpose. Figure 8 shows the result for the pendulum value.
The results for the macro-texture are reported in Figure 13.
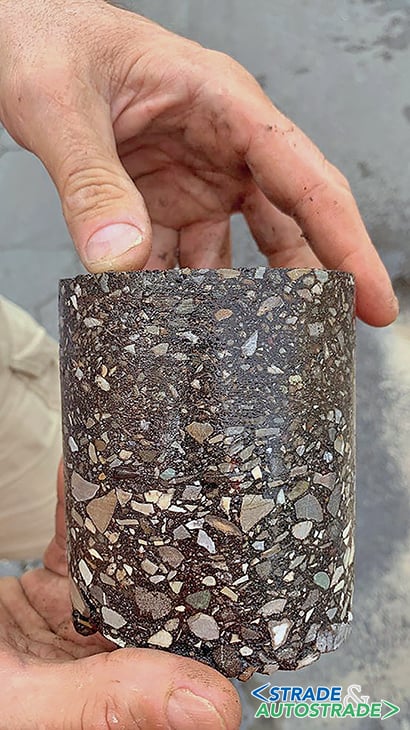
Tests on cores
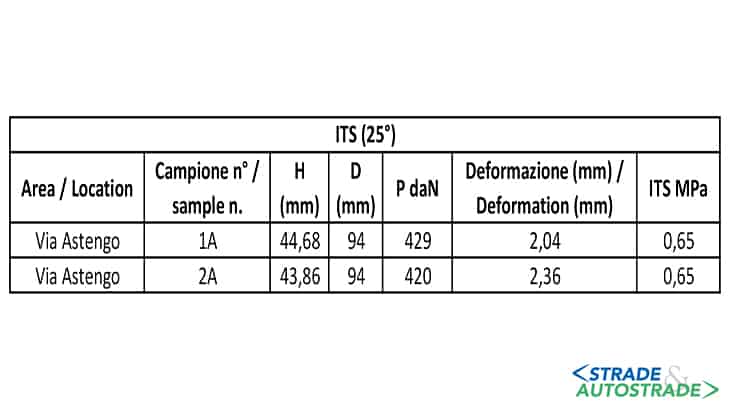
Various cores were taken at different job sites. Figure 14 is an example of the result in Via Astengo.

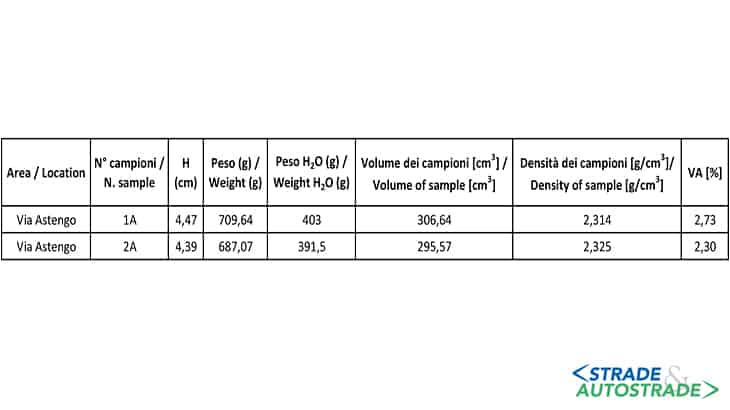
From a first visual analysis it is possible to observe that there is no clear separation between the new wear and the old pavement, an indication that the new layer is well bonded to the old underlying. Air voids content for each core is shown below. The results from the indirect tensile strength tests are shown in Figure 16.
Considering an ITS of 0.35 MPa as a reference value, the values are well beyond the requirement and therefore able to ensure adequate performance for the patch. To sum up, the Simex rehabilitation method translates into durability and safety.
Conclusions
All results in small and dynamic road construction jobsite: no need to deploy large machines, with no impact on traffic, minimal labor and a single vehicle carrying all the necessary equipment.
Furthermore, no material is carried from/to the site as the existing pavement is fully reused. A sustainable approach that simplifies the process by cutting down costs, reusing only existing materials that can be recycled again in subsequent maintenance cycles.
Numerous road maintenance is such an important issue that the implications are nowadays also of political nature. Very often the poor state of maintenance affects our roads safety as well as the ride comfort. In an advanced country, no exception should be allowed even on the latter, but certainly safety is the top priority. tests were carried out in Italy, in the Emilia Romagna region. Thanks to the collaboration with the University of Bologna, at the Department of Civil, Chemical, Environmental and Materials Engineering, these road sections have been subjected to investigation with core drilling, field tests and laboratory analyses.
The results indicate excellent performance values capable of guaranteeing the durability and safety of the rehabilitation. Some stretches have been subjected to traffic (heavy in some areas) for almost two years to prove the results achieved.
![]() Per la versione in Italiano: https://www.stradeeautostrade.it/attrezzature-e-componenti/la-rigenerazione-a-freddo-in-sito-dellasfalto-ammalorato-per-un-immediato-ripristino/
Per la versione in Italiano: https://www.stradeeautostrade.it/attrezzature-e-componenti/la-rigenerazione-a-freddo-in-sito-dellasfalto-ammalorato-per-un-immediato-ripristino/






